Table Of Content

Cost Per Mille (CPM) is a key metric in digital advertising, used to measure how much an advertiser pays for 1,000 impressions of an ad. The term "mille" comes from Latin, meaning "thousand," and Cost Per Mille refers to the cost for 1,000 views or clicks on an ad.
Cost-per-mille advertising is commonly used in display ads, social media campaigns, and other media buying strategies. It's important because it helps advertisers understand how much they'll spend to reach a large audience.
By tracking CPM, advertisers can better manage budgets and evaluate campaign effectiveness. It's a straightforward way to compare costs across different platforms and ad formats.
How Do You Calculate CPM?
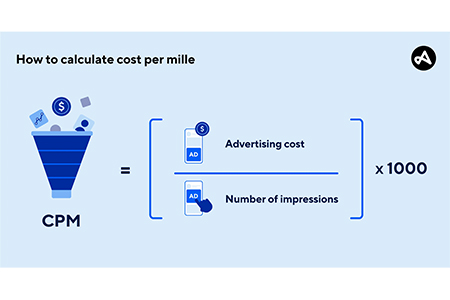
The CPM Formula
To calculate CPM, use this formula:
CPM = (Cost / Impressions) x 1000
This means you divide the total cost of the ad by the number of impressions (views or clicks) and then multiply by 1,000 to get the cost for 1,000 impressions.
Example Calculation
Let’s say you spent $500 on an ad, and it got 100,000 impressions.
CPM = (500 / 100,000) x 1000
CPM = 5
So, the cost for 1,000 impressions is $5.
Factors Influencing CPM
Several factors can affect CPM, including:
- Audience targeting: Ads shown to specific groups (e.g., age, location) can cost more.
- Ad placement: Popular sites or platforms like social media often have higher CPMs.
- Seasonality: During high-demand periods, like holidays, CPM rates may rise due to increased competition.
Understanding these factors helps advertisers make better decisions and optimize their ad budgets. By tracking CPM, advertisers can adjust strategies for cost-effective campaigns.
Importance of Cost Per Mille
Budget Management

Cost Per Mille (CPM) helps advertisers plan and control their budgets more effectively. By understanding the cost of 1,000 impressions, advertisers can predict how much their campaigns will cost based on the audience size they want to reach. This makes it easier to set spending limits and avoid overspending.
Performance Measurement

CPM plays a key role in measuring how well an ad campaign is performing. Since it focuses on impressions, advertisers can track how much they’re paying for each view or exposure. This gives a clear view of the cost of gaining visibility and helps determine if the campaign is reaching the right audience effectively.
Comparison with Other Pricing Models
CPM differs from other pricing models like CPC (Cost Per Click) and CPA (Cost Per Action). While CPC charges advertisers based on clicks and CPA charges based on specific actions (like purchases), CPM focuses on views. This makes CPM ideal for campaigns focused on brand awareness rather than direct clicks or actions. By comparing these models, advertisers can choose the one that aligns with their campaign goals.
Best Practices for Optimizing Your Ad Spend Effectively

1.Targeting the Right Audience

Audience segmentation is key to lowering your Cost Per Mille (CPM). By identifying specific groups who are most likely to engage with your ads, you can avoid wasting resources on irrelevant impressions, improving the overall efficiency of your ad spend.
2. A/B Testing
A/B testing helps you refine your ad creatives and placements. By comparing different versions of your ads, you can determine what resonates best with your audience, leading to higher engagement and lower costs. This step is essential for improving your cost per mille advertising.
3. Monitoring and Adjusting Campaigns

Regularly track your ad performance and make data-driven adjustments. Keeping a close eye on metrics helps you identify underperforming ads and optimize them. This can significantly reduce Cost Per Mille CPM measures, allowing you to make the most of every dollar spent.
Whether you're working with an advertising agency or managing in-house, these strategies are essential for driving results.
Difference Between CPC and CPM
|
Points |
CPC (Cost Per Click) |
CPM (Cost Per Thousand Impressions) |
|
Definition |
You pay each time a user clicks on your ad. It's performance-driven and ideal for campaigns aiming to drive traffic. |
You pay for every 1,000 times your ad is shown to users, regardless of clicks. It’s focused on increasing brand visibility. |
|
Focus |
Measures user interaction, aiming for engagement (clicks). |
Measures ad exposure, aiming for broader reach. |
|
Pricing Model |
CPC Formula: CPC=Total CostTotal Clicks\text{CPC} = \frac{\text{Total Cost}}{\text{Total Clicks}}CPC=Total ClicksTotal Cost You pay based on the number of clicks your ad receives. |
CPM Formula: CPM=Total CostImpressions×1000\text{CPM} = \frac{\text{Total Cost}}{\text{Impressions}} \times 1000CPM=ImpressionsTotal Cost×1000 You pay for every 1,000 views, regardless of click actions. |
|
Ideal For |
Best for campaigns focused on driving website visits, lead generation, or sales. |
Best for campaigns aimed at increasing brand awareness, reach, or audience exposure. |
|
Campaign Goal |
Focuses on conversion, aiming for clicks and actions. |
Focuses on reach, aiming for maximum impressions and visibility. |
Common Challenges with CPM
Ad Fraud

Ad fraud poses a serious issue for cost-per-mille (CPM) advertising. Fraudulent activities, such as fake impressions generated by bots, can significantly impact the effectiveness of CPM campaigns. Advertisers pay for these misleading impressions, which means their Cost Per Mille doesn’t reflect true engagement. This leads to wasted budgets and lower return on investment (ROI), undermining the value of Cost Per Mille.
Market Fluctuations
Cost Per Mille rates can be heavily influenced by changing market conditions. During high-demand periods, such as holidays, CPM rates often increase. On the flip side, during economic downturns, the demand for ads may drop, causing CPM rates to fall. These fluctuations make it difficult to maintain consistent ad costs, which can disrupt campaigns relying on stable Cost-per-mille rates.
Conclusion
Cost Per Mille (CPM) is a key advertising metric that represents the cost of 1,000 impressions or views of an ad. Cost per mille advertising helps advertisers understand how much they are paying to reach a broader audience, optimizing their marketing budget.
For brands, leveraging CPM is beneficial as it focuses on maximizing visibility and brand awareness. By using cost per mille cpm measures, brands can ensure that their ads are seen by a large audience, driving exposure without directly tying costs to specific actions like clicks. This is especially useful for brands seeking to build recognition and visibility across wide-reaching platforms.
Excellent Publicity is the ideal Advertising Agency for executing CPM strategies. With a deep understanding of advertising and advanced targeting techniques, we ensure that your brand gets optimal exposure at the right cost.
Contact Excellent Publicity to learn more.
FAQs
CPM stands for "Cost Per Thousand" impressions. It measures the cost advertisers pay per 1,000 views of their ad, helping them gauge the effectiveness of an ad campaign in terms of reach.
Not necessarily. A higher CPM might indicate better targeting or premium placements, but it’s important to balance it with conversions. Higher costs don’t always lead to higher return on investment (ROI).
To reduce CPM, refine your targeting, optimize ad creatives, test different bidding strategies, and focus on less competitive but high-performing audience segments to lower costs while maintaining ad effectiveness.
Industries like finance, technology, and healthcare tend to have higher CPM rates due to high competition, valuable audiences, and greater ROI potential, making advertisers willing to pay a premium for exposure.